As the name suggests, plant lights are lamps used for plants, simulating the principle that plants need sunlight for photosynthesis, emitting wavelengths of light for planting flowers, vegetables, and other plants to supplement or completely replace sunlight.At the same time, plant lights can also supplement general lighting in horticultural environments.
Due to potential safety risks such as electric shock, fire, and photo biological hazards, manufacturers need to create high-standard and high-safety products. A more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of potential safety risks is still needed.The guarantee of safety performance is the premise of designing and manufacturing products. Understanding the requirements of relevant laws and regulations can optimize the overall development process of products and minimize the potential safety hazards that may be brought to end users after entering the sales market.
Q1: What are the electrical safety evaluation standards for plant lights in the North American market?
A.
North American standard for plant lights: UL 8800 Horticultural Lighting Equipment And Systems
It is usually necessary to add the standard of the final luminaire to evaluate, for example:
Fixed plant light: UL 8800 + UL 1598
Portable plant light: UL 8800 + UL 153
Plant Bulbs: UL 8800 + UL 1993
Q2: Do plant lights need to meet energy efficiency requirements in addition to electrical safety certification for sales in the United States?
A.
To enter the US market, plant lights first need to obtain electrical safety certification from NRTL, the National Recognized Testing Laboratory.
At present, plant lights have not been included in the energy efficiency requirements of the US DOE, California CEC, and other countries.
Q3: What are the fire prevention requirements for the plastic housing of the North American certified plant lamp?
A.
According to UL 746C and the requirements for final lamps, different categories of lamps need to meet the following corresponding fire ratings, and also need to have outdoor protection f1 Rating.(f1: Suitable for outdoor use with respect to exposure to Ultraviolet Light, Water Exposure and Immersion in accordance with UL 746C.)
Fixed plant lamp: 5VA;
Portable plant light: HB, V-2, V-1, V-0, 5VB, 5VA can be used for household products;others require V-2, V-1, V-0, 5VB, 5VA;
Plant light bulb: V-0, 5VB, 5VA
Q4: Compared to ordinary lamps, what are the requirements for electrical safety compliance of plant lights?
A.
1. The ambient temperature assessment of the product is at least 40 degrees, that is, Ta≥40 degrees;
2. Hard-usage type power cords must be at least SJTW, and the power cords must meet outdoor use requirements;
3. Outdoor plant lights require a nominal waterproof IP rating of at least IP54;
4. The plastic housing of the plant lamp used outdoors needs to have an outdoor protection level of f1;
5. The product needs to meet the photobiological hazard test to ensure that its light radiation does not cause harm to the human body.
Q5: What are the requirements for internal wiring?
A.
The product should use a sufficient wire diameter and appropriate model of wire, and the internal wire must meet the UL 758 certification requirements. The following factors must be considered in the product design:
The possible tolerable voltage and temperature.Such information is also identified on the insulation layer of the internal wire;
The internal wires and connecting terminals should be surrounded by the shell;
The internal wire cannot contact metal edges or other sharp edges that may damage the insulation layer, as well as moving parts;
The diameter of internal wires must be selected according to the corresponding current-carrying capacity requirements in the following table:
| General Wiring Size and Ampacities
Wire diameter and current carrying capacity |
||
| mm² | AWG | Ampacity (A) |
| 0.41 | 22 | 4 |
| 0.66 | 20 | 7 |
| 0.82 | 18 | 10 |
| 1.3 | 16 | 13 |
Q6: What are the different risk levels for plant lighting biosafety requirements?
A.
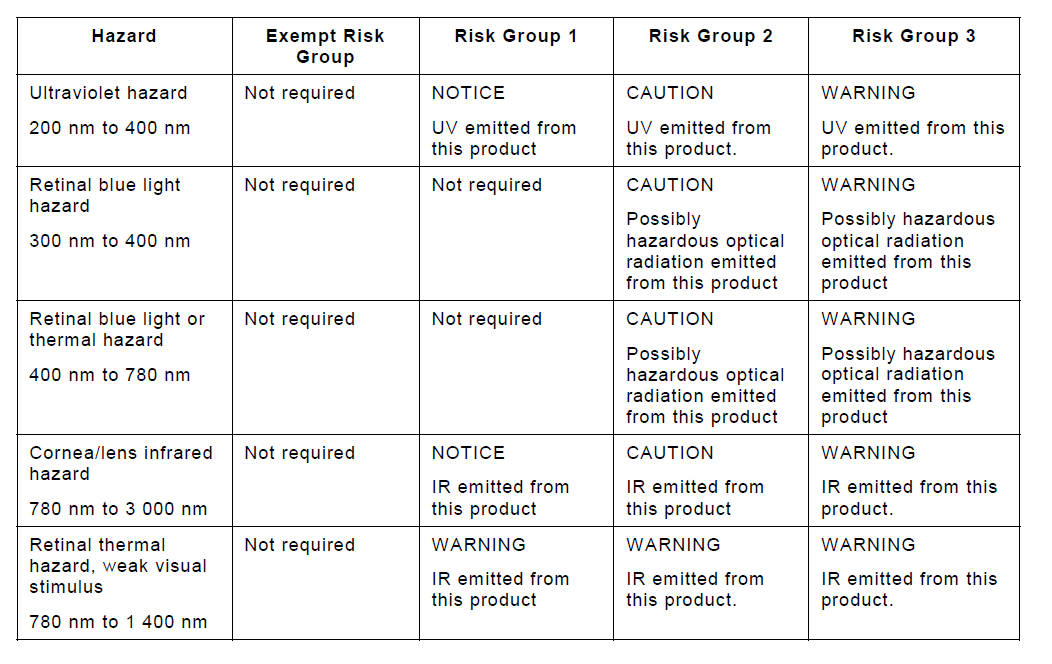
The wavelength of plant lighting lamps should generally be between 280 nm and 1400 nm. According to IEC 62471 photometric biohazards, UL8800 only accepts Risk group 0, Risk group 1, and Risk group 2, and does not accept light biohazard levels exceeding Risk group 2. Additionally, the product needs to be labeled accordingly based on the test results.
Q7: What are the notable abnormal tests during the certification process and how to judge the test results?
A.
Common fault tests include:
1) The product needs to pass a single failure test, such as a short circuit in the power supply circuit components,
2) Blocking the cooling fan and other abnormal tests.
The test results are determined as follows:
a) The overcurrent protection device of the distribution line cannot be disconnected during the test process
b) No flame is emitted or spread from the product shell
c) The tissue and gauze covered by the test process were not ignited, carbonized, or burned red
d) The 3A fuse connected in series to the ground connection is not disconnected
e) No risk of electric shock, fire or injury
If the protective device acts within 3 hours under fault testing conditions, the temperature of the product's mounting surface and contact surface is required to not exceed 160 degrees. If the protective device does not act within 3 hours, the temperature of the mounting surface and contact surface is required to not exceed 90 degrees after 7 hours.
Post time: Nov-08-2023