After July 1, 2006, the European Union reserves the right to conduct random inspections of electronic and electrical products sold in the market. Once a product is found to be inconsistent with the requirements of the RoHs Directive, the European Union has the right to take punitive measures such as suspension of sales, seals, and fines.
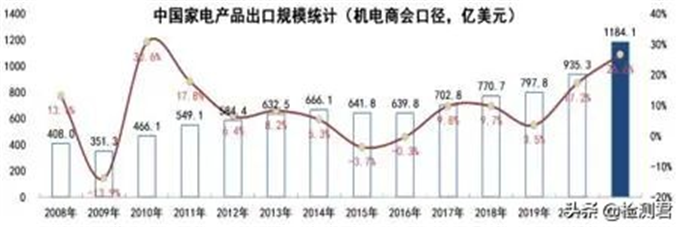
Affected by the epidemic, my country’s exports of home appliances hit a new high. According to statistics released by the General Administration of Customs, in 2021, China’s exports of household appliances reached US$98.72 billion, a year-on-year increase of 22.3%. Home appliances have also become the fourth one to exceed 100 billion US dollars after relay integrated circuits, mobile phones, and computers (including notebooks) products of electromechanical products (statistics from the China Chamber of Commerce for Import and Export of Mechanical and Electrical Products, the cumulative export of my country’s home appliance products will be 118.45 billion US dollars in 2021) Export-scale products.
China is one of the major manufacturers of home appliances. Home appliances are exported to more than 200 countries (or regions) on six continents in the world. Europe and North America are the main traditional markets for my country’s home appliance exports. After July 1, 2006, the European Union reserves the right to conduct random inspections of electronic and electrical products sold in the market. Once a product is found to be inconsistent with the requirements of the RoHs Directive, the European Union has the right to take punitive measures such as suspension of sales, seals, and fines. Therefore, if you manufacture, import or distribute goods covered by this Directive, the content of hazardous substances in the product must not exceed permitted levels.
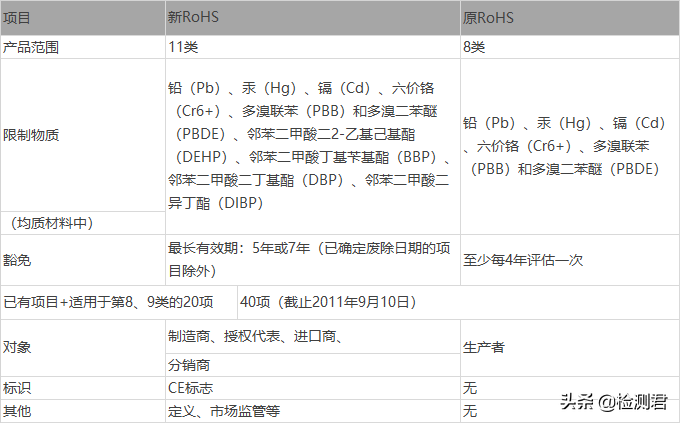
1. What is the RoHS Directive? In order to harmonize the laws of member states on the restriction of the use of hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, standardize the material and process standards of electrical and electronic products, make them more conducive to human health and environmental protection, and help waste electrical and electronic equipment comply with Environmental requirements for recycling and disposal, the European Union issued a directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment (2002/95/EC) on January 23, 2003, that is, the RoHS directive requires since July 1, 2006 Since then, all electrical and electronic equipment sold in the EU market must ban the use of heavy metals such as lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and flame retardants such as polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) and polybrominated biphenyl (PBB). It was replaced in 2011 by a new Directive (2011/65/EU). The new directive came into effect on January 3, 2013, and the original directive was repealed at the same time. According to the provisions of the new directive, from the date of the repeal of the original directive, all products under the CE mark must meet the requirements of low voltage (LVD), electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), energy-related products (ErP) and the new RoHS directive at the same time. To enter the EU market, companies exporting electrical and electronic equipment to a country in the EU need to comply with the specific laws of the exporting country.
2. What is the key content of the new RoHS directive? Compared with the original RoHS directive, the revised content of the new RoHS is mainly reflected in the following four aspects: First, the scope of controlled products has been expanded. Based on the eight categories of electrical and electronic equipment controlled by the original RoHS directive, it has been expanded to include medical equipment and monitoring equipment. For almost all electrical and electronic equipment, different execution times are specified for different product categories. Second, introduce a review and supplement mechanism for the list of restricted substances, regularly review and revise hazardous substances and their limits, and increase restricted substances in a more rigorous manner. When selecting restricted substances, attention should also be paid to the coordination with other regulations, especially the substances in Annex XIV (SVHC Authorization List) and Annex XVI (Restricted Substances List) of REACH Regulation, by indicating the scope of restricted substances for future evaluation. Allow more time and direction for businesses to select alternative materials. Third, clarify the exemption mechanism, give different exemption validity periods for different product categories to encourage enterprises to develop relevant alternatives, and adjust and update the exemption validity period according to the actual situation. Fourth, related to the CE mark, according to the requirements of the new RoHS directive, electrical and electronic equipment must not only meet the limit requirements of restricted substances, but also affix the CE mark before putting it on the market. The main difference between the old and the new RoHS directive
3. What are the scope of products controlled by the RoHS directive?
1. Large household appliances: refrigerators, washing machines, microwave ovens, air conditioners, etc., including the new RoHS new product categories “gas grill”, “gas oven” and “gas heater”.
2. Small household appliances: vacuum cleaners, electric irons, hair dryers, ovens, clocks, etc.
3. Information technology and communication equipment: computers, fax machines, telephones, mobile phones, etc.
4. User equipment: radios, televisions, video recorders, musical instruments, etc., including the new RoHS new product category “furniture with electrical functions”, such as “lifting reclining beds” and “lifting reclining chairs”.
5. Lighting equipment: Fluorescent lamps other than household lighting, etc., lighting control devices
6. Electrical and electronic tools (except large stationary industrial equipment): electric drills, lathes, welding, sprayers, etc.
7. Toys, leisure and sports equipment: electric vehicles, video game machines, automatic gambling machines, etc., including the new RoHS new product category “toys with minor electrical functions”, such as “talking teddy bears” and “talking teddy bears” Glowing Shoes”.
8. Medical equipment: radiation therapy apparatus, electrocardiogram tester, analytical instrument, etc.
9. Monitoring and control devices: smoke detectors, incubators, factory monitoring and control machines, etc.
10. Vending machines
11. Any other EEE that is not within the scope of the above categories: In addition to “power switch” and “electric suitcase”, including the new RoHS new product category “clothing with electrical functions”, such as “heated clothing” and “glows in water” life jackets”.
Products controlled by the RoHS directive include not only complete machine products, but also components, raw materials and packaging used in the production of complete machines, which are related to the entire production chain.
4. What are the requirements for hazardous substances and their limits? Article 4 of the new RoHS Directive stipulates that member states should ensure that electrical and electronic products placed on the market, including their cables and accessories for repair or reuse, or to update their functions or increase their capacity, do not contain lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), hexavalent chromium (Cr6+), polybrominated biphenyls (PBB) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) and other 6 hazardous substances. In 2015, the revised directive 2015/863/EU was issued, extending the new RoHS directive , increase DEHP (2-ethylhexyl phthalate), BBP (butyl benzyl phthalate), DBP (dibutyl phthalate), DIBP (diisobutyl phthalate) Four chemical substances called phthalates, such as phthalates), have entered the list of restricted chemical substances. After the revision of the directive, the types of hazardous chemical substances in electrical appliances controlled by the new RoHS directive have been increased to 10:
1. Lead (Pb) Examples of uses of this substance: solder, glass, PVC stabilizers 2. Mercury (Hg) (mercury) Examples of uses of this substance: thermostats, sensors, switches and relays, light bulbs 3. Cadmium (Cd ) Examples of use of this substance: switches, springs, connectors, housings and PCBs, contacts, batteries 4. Hexavalent chromium (Cr 6+) Examples of use of this substance: Metal anti-corrosion coatings Examples of this substance: flame retardants, PCBs, connectors, plastic housings 6. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE) Examples of using this substance: flame retardants, PCBs, connectors, plastic housings ethylhexyl ester) 8. BBP (butyl benzyl phthalate) 9. DBP (dibutyl phthalate) 10. DIBP (diisobutyl phthalate)
At the same time, the maximum content of harmful substances in homogeneous materials is: lead not exceeding 0.1%, mercury not exceeding 0.1%, cadmium not exceeding 0.01%, hexavalent chromium not exceeding 0.1%, polybrominated biphenyls not exceeding 0.1%, polybrominated diphenyl ethers not more than 0.1%. Four new chemicals called phthalates were added with a limit of 0.1% each.
5. What is the verification application process?
■ Step 1. Fill in the RoHS test application form, which can be collected from the RoHS verification center, or downloaded from the RoHS verification center website, and returned after filling. ■ Step 2. Quotation: After submitting the application, the customer sends the sample (or express delivery) to the verification unit, and the verification unit divides the sample reasonably according to the requirements, and returns the product split quantity and test fee to the customer. ■ Step 3. After the payment is received, the test will be arranged. Generally, the test will be completed within one week. ■ Step 4. Publish the report, which can be delivered by courier, fax, e-mail or the inspector in person.
6. How much does RoHS certification cost? The exact RoHS test price requires the company to provide product pictures and bill of materials, depending on the complexity of the product. RoHS certification is different from CCC, UL and other certifications. It only conducts chemical analysis tests for samples, so there is no factory inspection. If the products are not changed and the test standards are not updated, there will be no other follow-up costs.
7. How long does it take to do ROHS certification? At present, RoHS certification mainly tests 6 substances of lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, PBB and PBDE. Common products apply for ROHS certification. On the premise that customers provide samples and materials, the RoHS testing time for conventional products is about 7 days.
8. How long is the ROHS certification valid for? There is no mandatory validity period for ROHS certification. If the test standard of ROHS certification is not officially revised, the original ROHS certificate can be valid for a long time.
Post time: Aug-09-2022